Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Objective Important Questions Part 2 in English
Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Objective Important Questions Part 2 in English
BSEB 12th Chemistry Objective Important Questions Part 2 in English
Question 1.
The general electronic configuration of inner transition elements is :
(a) (n-2)f1-7(n-1)d1ns1
(b) (n-2)f1-14(n-1)d0 or 1 ns1
(c) (n-2)f1-14(n-1)a0 or 1 ns2
(d) none
Answer:
(c) (n-2)f1-14(n-1)a0 or 1 ns2
Question 2.
In the first transition series the highest oxidation state is exhibited by:
(a) Mn
(b) Ni
(c) Fe
(d) Cr
Answer:
(a) Mn
Question 3.
Brass is an alloy containing
(a) Cu and Zn
(b) Cu and Sn
(c) Zn and S
(d) Cu, Zn and Sn
Answer:
(a) Cu and Zn
Question 4.
Iron ores are concentrated by:
(a) gravity separation process
(b) froth floatation method
(c) amalgamation
(d) handpicking
Answer:
(a) gravity separation process
Question 5.
Purest form of iron is :
(a) pig iron
(b) cast iron
(c) wrought iron
(d) steel
Answer:
(c) wrought iron
Question 6.
Green vitriol is :
(a) ZnSO4. 7H2O
(b) FeSO4. 7H2O
(c) CuSO4. 5H2O
(d) Na2SO4. 10H2O
Answer:
(b) FeSO4. 7H2O
Question 7.
Vitamin-B12 contains:
(a) CO3+
(b) Cu2+
(c) Zn2+
(d) Fe2+
Answer:
(a) CO3+
Question 8.
Primary amine on treatment with NaNO2 and HCl yields :
(a) nitro compound
(b) ammonia
(c) secondary alcohol
(d) primary alcohol
Answer:
(d) primary alcohol
Question 9.
Ethyl alcohol is obtained when ethyl chloride is boiled with:
(a) alcoholic
(b) aqueous KOH
(c) water
(d) H2O2
Answer:
(b) aqueous KOH
Question 10.
Which of the following does not give iodoform?
(a) CH3OH
(b) C2H5OH
(c) CH3CHO
(d) CH3COCH3
Answer:
(a) CH3OH
Question 11.
An alkyl halide reacts with metallic sodium in dry ether. The reaction is known as :
(a) Frankland’s reaction
(b) Sandmeyer’s reaction
(c) Wurtz reaction
(d) Wurtz-Fittig reaction
Answer:
(c) Wurtz reaction
Question 12.
Which gives iodoform test?
(a) Propanone
(b) butanone
(c) 2-pentanone
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 13.
Which is detected by carbyl amine test?
(a) NH2 . CO. NH2
(b) CH3CONH2
(c) C2H5NH2
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c) C2H5NH2
Question 14.
Which of the following will give a yellow precipitate with I2 and NaOH?
(a) ICH2COOCH2CH3
(b) CH3COOCOCH3
(c) CH3CONH2
(d) CH3CH (OH)CH2CH3
Answer:
(d) CH3CH (OH)CH2CH3
Question 15.
Which one is a primary alcoholic group?
(a) -CH2OH
(b) > CH . OH
(c) > C – OH
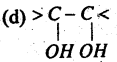
Answer:
(a) -CH2OH
Question 16.
Monohydric alcohols have the general formula :
(a) CnH2nO
(b) CnH2n+1O
(c) CnH2n+2O
(d) CnH2n+4
Answer:
(c) CnH2n+2O
Question 17.
Which one of the following alcohols reacts most readily with-lucas reagent?
(a) CH3. CH2 CH2OH
(b) (CH3)2CHOH
(c) (CH3)3COH
(d) CH3.CH2OH
Answer:
(c) (CH3)3COH
Question 18.
Butan-2-ol is a :
(a) primary alcohol
(b) secondary alcohol
(c) tertiary alcohol
(d) dihydric alcohol
Answer:
(b) secondary alcohol
Question 19.
Ethyl alcohol oh oxidation with dil. acidic K2Cr2O7 solution finally gives:
(a) formic acid
(b) formaldehyde
(c) acetic acid
(d) acetaldehyde
Answer:
(c) acetic acid
Question 20.
Which of the following enzymes converts glucose into ethyl alochol:
(a) diastase
(b) invertase
(c) maltase
(d) zymase
Answer:
(d) zymase
Question 21.
Which of the following chemicals Is used for the denaturation of ethyl alcohol:
(a ) CH3OCH3
(b) Pyridine
(c) anhydrous CaCl2
(d) naphtha
Answer:
(b) Pyridine
Question 22.
Williamson’s synthesis is used to prepare :
(a) ethers
(b) acetone
(c) PVC
(d) backelite
Answer:
(a) ethers
Question 23.
Dry distillation of calcium acetate will give :
(a) CH3COOH
(b) CH3COCH3
(c) HCHO
(d) CH3CHO
Answer:
(b) CH3COCH3
Question 24.
Dry heating of a mixture of calcium acetate and calcium formate yields:
(a) acetone
(b) acetaldehyde
(c) formic acid
(d) formaldehyde
Answer:
(b) acetaldehyde
Question 25.
Which of following classes of compounds gives Tollins reagent test?
(a) alcohols
(b) aldehydes
(c) ketones
(d) ethers
Answer:
(b) aldehydes
Question 26.
Aldehydes and ketones may be distinguished by :
(a) Lucas reagent
(b) Tollen’s reagent
(c) Baeyer’s reagent
(d) Fenton’s reagent
Answer:
(b) Tollen’s reagent
Question 27.
An aldehyde on oxidation gives :
(a) an acid
(b) an alcohol
(c) an ether
(d) an ester
Answer:
(a) an acid
Question 28.
Vitamin C is:
(a) ascorbic acid
(b) nicotinic acid
(c) citric acid
(d) tartaric acid
Answer:
(a) ascorbic acid
Question 29.
Enzymes are:
(a) Proteins
(b) Lipids
(c) Carbohydrates
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Proteins
Question 30.
Rickets is caused due to deficiency of:
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin B
(c) Vitamin C
(d) Vitamin D
Answer:
(d) Vitamin D
Question 31.
Which of the following is an antibiotic:
(a) terramycin
(b) aspirin
(c) paracetamol
(d) chloroquine
Answer:
(a) terramycin
Question 32.
Which of the following is used as an antipyretic?
(a) paracetamol
(b) chloroquine
(c) terramycin
(d) chloramphenicol
Answer:
(a) paracetamol
Question 33.
Reserpine is
(a) tranquillizer
(b) antibiotic
(c) Vitamin
(d) harmone
Answer:
(a) tranquillizer
Question 34.
Terylene is:
(a) polyamide
(b) polyethylene
(c) polyester
(d) polyvinyl chloride
Answer:
(c) polyester
Question 35.
Orion is a ploymer of:
(a) styrene
(b) vinyl chloride
(c) tetrafluoroethene
(d) acrylonitrile
Answer:
(d) acrylonitrile
Question 36.
The monomer of teflon is :
(a) monofluoro ethene
(b) difluoro ethene
(c) trifiuoroethene
(d) tetrafluoro ethene
Answer:
(d) tetrafluoro ethene
Question 37.
Which one of the following is a thermosetting plastic?
(a) PVC
(b) PVA
(c) Bakelite
(d) Perspex
Answer:
(c) Bakelite
Question 38.
Chloroquine is:
(a) an analgesic
(b) antibiotic
(c) an antimalarial
(d) an antipyretic
Answer:
(c) an antimalarial
Question 39.
Morphine is:
(a) antiseptic
(b) analgesic
(c) antibiotic
(d) anaesthetic
Answer:
(b) analgesic
Question 40.
Phenol is used as:
(a) an antiseptic
(b) an insecticide
(c) a disinfestant
(d) styptic
Answer:
(a) an antiseptic
Question 41.
Tranquillizers are used for the treatment of:
(a) Cancer
(b) AIDS
(c) Mental diseases
(d) Blood infection
Answer:
(c) Mental diseases
Question 42.
Lucas reagent is:
(a) anhydrous ZnCl2 and conc. HCl
(b) MnO2
(c) H2SO4 and HCl
(d) Na + H2O
Answer:
(a) anhydrous ZnCl2 and conc. HCl
Question 43.
Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are distinguished by :
(a) Oxidation method
(b) Lucas test
(c) Victor Meyer’s method
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 44.
CH3OH and C2H5OH may be distinguished chemically :
(a) by the action of HCl
(b) By iodoform test
(c) by the action of NH3
(d) solubility in water
Answer:
(b) By iodoform test
Question 45.
The oxidation state of Ni in Ni(CO)4 is :
(a) +1
(b) +2
(c) +4
(d) 0
Answer:
(d) 0
Question 46.
Iodoform is formed on warming iodine and sodium hydroxide with :
(a) CH3OH
(b) HCOOH
(c) C2H5OH
(d) C2H6
Answer:
(c) C2H5OH
Question 47.
The catalyst used in the manufacture of sulphuric by lead chamber process is:
(a) Pt
(b) Ni
(c) NO
(d) N2O3
Answer:
(c) NO
Question 48.
The catalyst used in the manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process:
(a) platinised asbestos
(b) Ni
(c) Fe
(d) NO
Answer:
(a) platinised asbestos
Question 49.
Bleaching action of SO2 is due to :
(a) reduction
(b) oxidation
(c) its acidic nature
(d) hydrolysis
Answer:
(a) reduction
Question 50.
Cara’s acid is :
(a) H2SO5
(b) H2SO3
(c) H3S2O5
(d) H2S2O8
Answer:
(a) H2SO5
Question 51.
Marshall’s add is:
(a) H2S2O5
(b) H2S2O5
(c) H2SO5
(d) H2SO4
Answer:
(b) H2S2O5
Question 52.
Sulphur dioxide is:
(a) only reducing agent
(b) only oxidising agent
(c) both oxidising and reducing agent
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) both oxidising and reducing agent
Question 53.
SO2 is:
(a) acidic
(b) basic
(c) neutral
(d) ampholeric
Answer:
(a) acidic
Question 54.
Which compound acts as an oxidising as well as a reducing agent?
(a) SO2
(b) SO3
(c) CrO3
(d) MnO2
Answer:
(a) SO2
Question 55.
The acid used in lead storage cell is :
(a) Phosphoric
(b) sulphuric acid
(c) hydrochloric
(d) nitric acid
Answer:
(b) sulphuric acid
Question 56.
Which one of the following is the strongest acid?
(a) HF
(b) HI
(c) HBr
(d) HCl
Answer:
(b) HI
Question 57.
Which one of the following is the strongest acid :
(a) HClO
(b) HClO2
(c) HClO3
(d) HClO4
Answer:
(d) HClO4
Question 58.
Which is the strongest oxidising agent?
(a) HCl
(b) HClO2
(c) HClO3
(d) HClO4
Answer:
(a) HCl
Question 59.
Which one of the following has hydrogen bonding?
(a) HCl
(b) HBr
(c) HF
(d) HI
Answer:
(c) HF
Question 60.
The catalyst used in the deacon’s process for the manufacture of chlorine is:
(a) Cu
(b) An alloy of copper
(c) CuCl2
(d) CuS
Answer:
(c) CuCl2
Question 61.
Which one of the following acts as an antichlor :
(a) MnO2
(b) Na2S2O3
(c) K2Cr2O7
(d) Na2SO4
Answer:
(b) Na2S2O3
Question 62.
Slaked lime reacts with chlorine to form :
(a) Ca(OCl)Cl
(b) Ca(OCl)2
(c) Ca(ClO3)2
(d) CaCl2
Answer:
(a) Ca(OCl)Cl
Question 63.
The chemical name of bleaching powder is :
(a) Calcium hypochlorite
(b) Calcium chloro hypochlorite
(c) Calcium chlorate
(d) Calcium perchlorate
Answer:
(b) Calcium chloro hypochlorite
Question 64.
Which of the following elements does not belong to first transition series?
(a) Fe
(b) V
(c) Cu
(d) Ag
Answer:
(d) Ag
Question 65.
Transition elements are:
(a) s-block
(b) p-block
(c) d-block
(d) f-block
Answer:
(c) d-block
Question 66.
Dettol is:
(a) an antiseptic
(b) an antibiotic
(c) a tranquillizer
(d) an analgesic
Answer:
(a) an antiseptic
Question 67.
Paracetamol is :
(a) antihistamine
(b) antimalarial
(c) antipyretic
(d) tranquillizer
Answer:
(c) antipyretic
Question 68.
Which one of the following is a tranquillizer?
(a) barbituric acid
(b) aspirin
(c) chloroquine
(d) penicillin
Answer:
(a) barbituric acid
Question 69.
Which one of the following is an anti-histamine?
(a) Diphenhydramine
(b) aspirin
(c) chloroquine
(d) streptomycin
Answer:
(a) Diphenhydramine
Question 70.
The most common oxidation state shown by first row transition elements is:
(a) + 2
(b) + 3
(c) + 4
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) + 2
Question 71.
Chloral is:
(a) CCl3CHO
(b) CCl3CH3
(c) CCl3COCH3
(d) CCl3CH2OH
Answer:
(a) CCl3CHO
Question 72.
Amongst the following the most reactive alkyl halide is :
(a) C2H5Br
(b) C2H5I
(c) C2H5Cl
(d) All are same
Answer:
(a) C2H5Br
Question 73.
Amongst the following which one is the most reactive?
(a) CH3CH2I
(b) C2H5Br
(c) (CH3)3Cl
(d) All are same
Answer:
(c) (CH3)3Cl
Question 74.
Ethyl iodide on treatment with moist silver oxide gives :
(a) acetic acid
(b) ethyl alcohol
(c) acetaldehyde
(d)none
Answer:
(b) ethyl alcohol
Question 75.
Amongst the following, the one having the highest boiling point is :
(a) C2H5Cl
(b) C2H5Br
(c) C2H5I
(d) CH3Cl
Answer:
(c) C2H5I
Question 76.
Which one of the following will give ethyl alcohol when heated with moist silver oxide:
(a) CH3I
(b) C2H5Br
(c) (CH3)2CHI
(d) CH3-CH2-CH2I
Answer:
(b) C2H5Br
Question 77.
Amongst the following which one has the highest boiling point?
(a) ethyl alcohol
(b) n-propyl alcohol
(c) n-butyl alcohol
(d) methyl alcohol
Answer:
(c) n-butyl alcohol
Question 78.
Which one is the most acidic?
(a) CH3OH
(b) C2H5OH
(c) CH3·CH(OH)·CH3
(d) CH3·CH2·CH2OH
Answer:
(a) CH3OH
Question 79.
Ethyl alcohol, when oxidised with acidic K2Cr2O7 solution, gives:
(a) CH3·COOH
(b) HCOOH
(c) CH3·CO·CH3
(d) None
Answer:
(a) CH3·COOH
Question 80.
Which one of the following will give an aldehyde on oxidation with chromic anhydride in glacial acetic acid?
(a) CH2COOH
(b) CH3CH(OH)CH3
(c) CH3 CH2OH
(d) None
Answer:
(c) CH3 CH2OH
Question 81.
Which one of the following will give a ketone on oxidation with acidic K2Cr2O7 ?
(a) CH3 CH2OH
(b) CH3CH (OH)CH3
(c) CH3OH
(d) None
Answer:
(b) CH3CH (OH)CH3
Question 82.
Which one of the following reduces Fehling’s solution?
(a) CH3COOH
(b) CH3COCH3
(c) HCHO
(d) CH3OH
Answer:
(c) HCHO
Question 83.
Which one of the following undergoes Cannizzaro reaction?
(a) HCHO
(b) CH3 CHO
(c) CH3COCH3
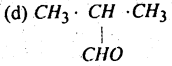
Answer:
(a) HCHO
Question 84.
Dry distillation of calcium acetate will give :
(a) CH3 COOH
(b) CH3COCH3
(c) CH3 CHO
(d) CH3 · CH3
Answer:
(b) CH3COCH3
Question 85.
Which will turn blue litmus red?
(a) HCOOH
(b) CH3CHO
(C) CH3COCH3
(d) None
Answer:
(a) HCOOH
Question 86.
When a mixture of calcium acetate and calcium formate is heated. it yields:
(a) acetone
(b) formic acid
(e) acetic acid
(d) acetaldehyde
Answer:
(d) acetaldehyde
Question 87.
Carboxylic acids do not give the characteristic properties of:
(a) >C = O group
(b) -COOH group
(c) Alkyl group
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) >C = O group
Question 88.
Which one is a phenol?
(a) C6H5CH2OH
(b) C6H5OH
(c) CH3CH2OH
(d) None
Answer:
(b) C6H5OH
Question 89.
Which is the strongest acid
(a) p-phenol
(b) m-phenol
(c) o-phenol
(d) phenol
Answer:
(a) p-phenol
Question 90.
Which of the following turns litmus red?
(a) CH3CH2OH
(b) C6H5CHO
(c) C6H5OH
(d) None
Answer:
(c) C6H5OH
Question 91.
Phenols do not react with :
(a) NaOH
(b) KOH
(c) NaHCO3
(d) None
Answer:
(c) NaHCO3
Question 92.
Amongst the following the most acidic oxide is:
(a) Sb2O5
(b) P2O5
(c) N2O5
(d) AS2O5
Answer:
(c) N2O5
Question 93.
The cause of variable valency-among transition dementias:
(a) They all exist in more than one oxidation state
(b) They all form complex compounds
(c) the valence electrons of them are found in two different subshells
(d) they all have paired electrons
Answer:
(c) the valence electrons of them are found in two different subshells
Question 94.
Which one is not a transition element?
(a) Co
(b) V
(c) Ge
(d) Rh
Answer:
(c) Ge
Question 95.
Froth floatation process is used :
(a) for calcination of ores
(b) for roasting of ores
(c) for concentration of ores
(d) for smelting of ores
Answer:
(c) for concentration of ores
Question 96.
Sulphide ores are concentrated by :
(a) gravity separation
(b) electromagnetic separation
(c) froth floatation process
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) froth floatation process
Question 97.
Froth floatation process is used for the concentration of:
(a) sulphide ores
(b) carbonate ores
(c) oxide ores
(d) sulphate ores
Answer:
(a) sulphide ores
Question 98.
Which of the following ores is concentrated by froth floatation process:
(a) Bauxite
(b) cassiterite
(c) galena
(d) siderite
Answer:
(c) galena
Question 99.
When one Faraday of Electric current is passed. The Mass deposited is equal to :
(a) One gram equivalent
(b) One gram Mole
(c) Electro-chemical equivalent
(d) Half gram equivalent
Answer:
(a) One gram equivalent
Question 100.
Amongst the following the most acidic oxide is :
(a) N2O3
(b) N2O5
(c) N2O4
(d) All are same
Answer:
(b) N2O5
Question 101.
Thermally most stable oxide is :
(a ) P2O3
(b) As2O3
(c) Sb2O3
(d) N2O3
Answer:
(d) N2O3
Question 102.
Which is the most stable:
(a) N2O3
(b) N2O5
(c) N2O4
(d) All are same
Answer:
(a) N2O3
Question 103.
Which one is the most basic?
(a) NH3
(b) AsH3
(c) SbH3
(d) PH3
Answer:
(a) NH3
Question 104.
Which one is the most stable?
(a) PH3
(b) NH3
(c) SbH3
(d) AsH3
Answer:
(b) NH3
Question 105.
Which is stronger reducing agent?
(a) PH3
(b) NH3
(c) SbH3
(d) AsH3
Answer:
(c) SbH3
Question 106.
Which of the folIowingeOmpounds is least acidic?
(a) H2Se
(b) H2O
(c) H2S
(d) H2Te
Answer:
(b) H2O
Question 107.
Which of the following compounds is most stable?
(a) H2O
(b) H2Te
(c) H2S
(d) H2Se
Answer:
(a) H2O
Question 108.
Which of the following is the strongest reducing agent?
(a) H2O
(b) H2Se
(c) H2Te
(d) H2S
Answer:
(c) H2Te
Question 109.
Which of the following aqueous solution should have highest boiling point:
(a) 1.0 M NaOH
(b) 1.0 M Na2SO4
(c) 1.0 M NH4NO3
(d) 1.0 M KNO3
Answer:
(b) 1.0 M Na2SO4
Question 110.
A solution has an osmotic pressure of 0.0821 atm at 300K. Its concentration would be:
(a) 0.66 M
(b) 0.32 M
(c) 0.066 M
(d) 0.0033 M
Answer:
(d) 0.0033 M
Question 111.
Azeotropic mixture of HCl and H2O has :
(a) 48% HCl
(b) 22.2% HCl
(c) 36% HCl
(d) 20.2% HCl
Answer:
(d) 20.2% HCl
Question 112.
The rate at which a substance reacts depends upon its:
(a) Atomic mass
(b) Equivalent mass
(c) Molecular mass
(d) Active mass
Answer:
(d) Active mass
Question 113.
Which of the following is Tribasic :
(a) H3PO2
(b) H3PO3
(c) H4P2O7
(d) H3PO4
Answer:
(d) H3PO4
Question 114.
Froth floatation process is based on :
(a) specific gravity of ore particles
(b) magnetic properties of the ore particles
(c) electrical properties of the ore particles
(d) wetting properties of the ore particles
Answer:
(d) wetting properties of the ore particles