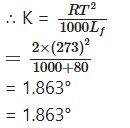Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Numericals Important Questions with Solutions in English
Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Numericals Important Questions with Solutions in English
BSEB 12th Chemistry Numericals Important Questions with Solutions in English
Question 1.
The decomposition of H2O2 was studies by titrating is at different intervals of time with KMnO4 Calculate the velocity constant for it from the following data, if the reaction is of the first order.
![]()
Solution:
The first order rate expression is :
![]()
The amount of KMnO4 is proportional to the amount of H2O2 present., so the volume of KMnO4 used at zero time corresponds to initial concentration (a) and the volume used after time, corresponds to (a-x) at that time. Inserting these values in the above equation, we get-

Question 2.
The optical reaction of sucrose in presence of dil HCl at various intervals is given in the following table:
![]()
Show that the reaction is of the first order.
Solution:
The inversion of sucrose will be a first order reaction if the above date confirms to the equation:
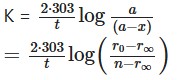
Where, r0, r1 and r∞ are the optical rotation and the start of the reaction, after t and at the completion of rerion respectively.
Inserting the values in the above equation, we get-
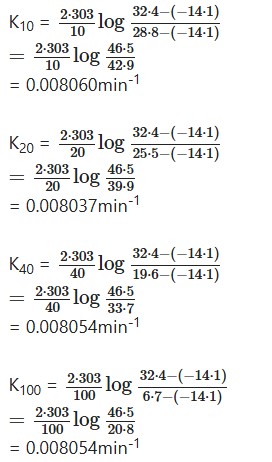
The constancy in the value of K shows that the reaction is of first order.
Question 3.
Decomposition of diazobenzene chloride was followed at constant temperature by measuring the volume of nitrogen evolved at different times.
The date is given below
![]()
Calculate the specific reaction rate and order of reaction
Solution:
Diazobenzene chloride decomposition as:
C6H5 – N = N-Cl → C6H5Cl + N2
Thus the amount of N2 evolved will be a measure ofdiazobenzene chloride decomposed i.e.x. The total N23 evolved at infinite time will thus give the initial concentration i.e. a. Now substituting the values in the first order rate
expression,
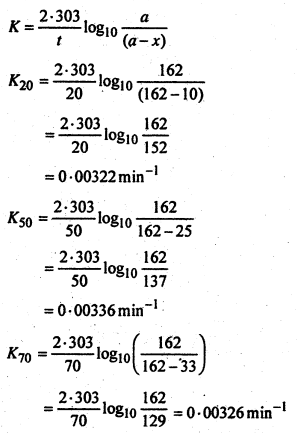
The constancy in the value of K shows that the reaction ¡s of the first order. The specific rate constant K is thus given by:
![]()
= 0.00328min-1
Question 4.
A first order reaction is 15% complete in 20 minutes. How long will it take to be 60% complete?
Solution:
For a first order reaction, we have-
![]()
or,
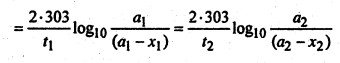
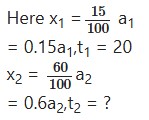
Inserting these values in equation (1), we get-
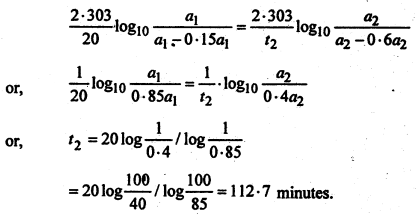
Question 5.
Given that the temperature co-efficient for the saponification of ethyl acetate by NaOH is 1.75. Calculate the activation energy.
Answer:
Given that-

Colligative Properties of Solutions
Osmotic Pressure
Question 6.
Calculate the value of R in litre-atomosphere, if the osmotic pressure of a solution containing 45g. of sucrose dissolved per liter of solution at 2° C is 3.0 atmospheres.
Solution:
The mol wt. (m) of sucrose (C12H22O11)
= 12 × 12 + 1 × 22 + 16 × 11
= 342
T = 2 + 273
= 275 K
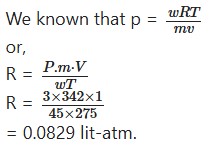
Question 7.
Calculate the osmotic pressure of 5% solution of glucose C6 H12O6 at 18° C.
Solution:
Given that, T = ( 18+273) = 291 K, w = 5g

Question 8.
A 1.02 % solution of glycerine is isotonic with 2% solution of glucose. What is the molecular weight of glycerine?
Solution:
For isotonic solution we have

or,

Question 9.
A solution containing 8.6 g/litre of urea (mol. wt. = 60) was found to be isotonic with a 5% solution of an organic solute. Calculate the molecular weight of the solute.
Solution:
For isotomic solution, we have-
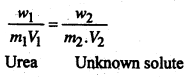
or,
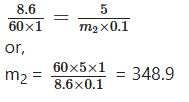
Question 10.
10 g of a substance dissolved in 100 ml of water gave rise to an osmotic pressure 500 cm of Hg at 27°C. Calculate the molecular weight of the substance.
Solution- We know that-

Question 11.
Calculate the amount of urea dissolved per litre if its equeour Solution is isotonic with 10% cane sugar. Molecular weight of urea = 60.
Solution:
For urea = m1 = 60; V1 = 1 litre, w1 = ?
For cane sugar = w2 = 10 g; m2 = 342, V2= 0.1 lit.
For isotonic solution:
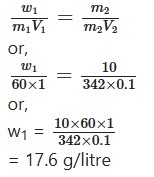
Question 12.
At 298 K, 100 ml of a solution containing 3.002g of an unidentified solute exhibts an osmotic pressure of 2.25 atm. What is the molecular mass of the solute.
Solution:
Given that V = 100 ml = 0.1 litre, w = 3.002g, m = ?
T = 298 K,P = 2.25 atm and R = 0.0821
We know that
![]()
Lowering of Vapour Pressure
Question 13.
A current of dry air was drawn through solution of 3.5 g of a ubstance in 100g of ethyl alcohol and then passed through ethyl alcohol lone. The loss of weight of the solution was 0.8759 g and of the alcohol 0241g.Calculate the molecular weight of dissolved substance.
Solution:
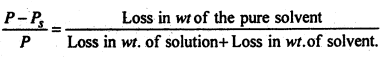

Question 14.
At 20°C the vapour pressure of ether is 442 m.m. when 6.1g of Benzoic acid are dissolved in 50g of ether, the vapour pressure falls to 410 m.m. What is the molecular weight of Benzoic acid?
Solution:
According to Rault’s law-

Question 15.
Dry air was drawn in succession thought a series of bulbs containing 4.27g of a substance X in 52.68g of ethyl alcohol and through similar set of bulbs containing pure alcohol, the indrawn air and the two sets of bulbs were at the same ‘constant temperature. The. loss of weight in first series of bulbs was 1.292g. and in second series .0313g. Calculate the mole wt.of X.
Solution:


Question 16.
Air was drawn through a solution containing 38g of solute in 100g of water and then through water. The loss of weight of water was .0551 g and the total weight of water absorbed in sulphuric acid tube was 2.2117g. Find the molecular weight of the dissolved substance.
Solution:

Question 17.
Dry air was passed through a solution containing 50g of a solute in 100g of water and then through water. The loss in weight of water is 0.05g. The wet air then passed through sulphuric acid whose weight increased by 2.00g. What is the molecular weigh t of the dissolved substance.
Solution:
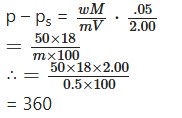
Elevation of Boiling Point
Question 18.
The boiling point of a solution Of 3.40 gms. of BaCl2 (Mol. wt. 208,4) in 100 gms. of water is 100.208°C. Calculate the degree of dissociation BaCl2 if the molecular elevation for water is 5.2.
Solution:
Calculation of observed mol. wt.
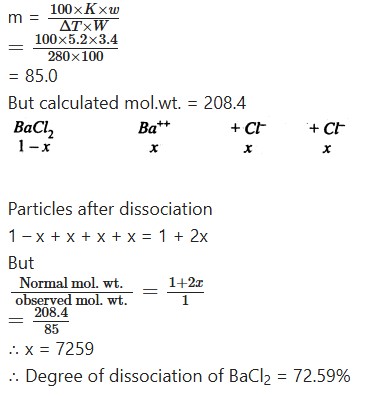
Question 19.
1.23 g of a substance dissolved in 10g of water raised the boiling point by 0.39″C. Calculate the molecular weight (K = 5.2°C)
Solution:
We know that:
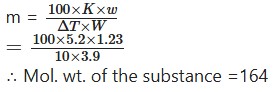
Question 20.
1.55 g of urethane dissolved in 34.22g of methyl alcohol raised the boiling point by 0.23″. The elevation constant for methyl alcohol is 8.8. Calculate the molecular weight of urethane.
Solution:
As given in the question, we have-
w = 1 .55 g Δt = 0.32°
W = 34.22g = 8.8
![]()
∴ Mol wt. of urethane = 124.6.
Question 21.
If the boiling point of water is raised by 0.071° by dissolving 1.17 g of cane sugar (C12 H22O11) in 25g of the solvent, find out the molecular elevation of boiling point
Solution:
As given in the question,
w = 1.17 gm ΔT = .071°
W = 25 gm m = mol. wt. of cane sugar
= 144 + 22+ 176 = 342
Now
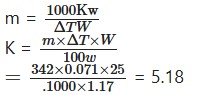
Hence the molecular elevation of boiling point = 518
Question 22.
The boiling point of a solution of 0.105g Of substance in 7.92g of ether was higher than that of the pure solvent by 0.2°. Find the mol wt. of the solute (Kb = 21.1)
Solution:
We know that-
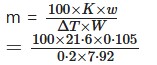
= 139.8
∴ Mol, wt. of the substance = 139.8
Depression in Freezing Point
Question 23.
Calculate the molar depression constant of water.
Solution:
Latent heat of fusion (LJ) = 80.0 Cal/g
Freezing point of water (T) = 0°C = 0 + 273 = 273°A