Bihar Board 12th Accountancy Important Questions Short Answer Type Part 2 in English
Bihar Board 12th Accountancy Important Questions Short Answer Type Part 2 in English
BSEB 12th Accountancy Important Questions Short Answer Type Part 2 in English
Question 1. What a meant by Partnership?
Answer: Meaning of Partnership: When two or more persons enter into an agreement for setting up a business, to fun it and share the profits and losses, it is termed as partnership.
As per Section 4 of the Partnership Act, 1932 :
“Partnership is the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all.”
This definition highlights following three elements or conditions to determine whether an association of persons is a partnership or whether a person is a partner in a firm :
- There must be an agreement between all the partners;
- The agreement must be to share the profit of a business; and
- The business must be carried on either by all partners or any of them acting for all.
Question 2. Write four items relating to not-for-profit organisation.
Answer: There are four items relating to Not for profit organisation are as follows :
- Subscription
- Donation
- Legacies
- Honorarium.
Question 3. Under which circumstances of a partnership firm is deemed to be dissolve.
Answer: The main reasons of dissolution of partnership firm are as following :
- On retiring of a partner
- On death of a partner
- On insolvent of a partner
- On the situation of oldness of enterprise
- On in liable of a partner.
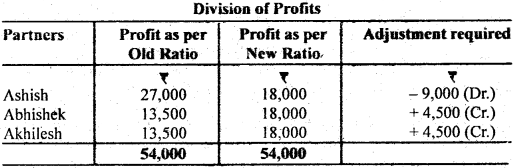
Question 4. Ashish, Abhishek and Akhilesh have been sharing profits in the ratio 2 : 1 : 1 respectively in a firm. The firm has existed for some years. Sow they decide to share profits equally and that too, with retrospective effect from 2013. The profits for the last three years were: 2013 – ₹ 20,000, 2014 – ₹ 10,000, 2015 – ₹ 16,000. Show the adjustment of profits for the last three years by means of Journal entries.
Answer:
Total profits of last three years
= ₹ 20,000 + 18,000 + 16,000
= ₹ 54,000

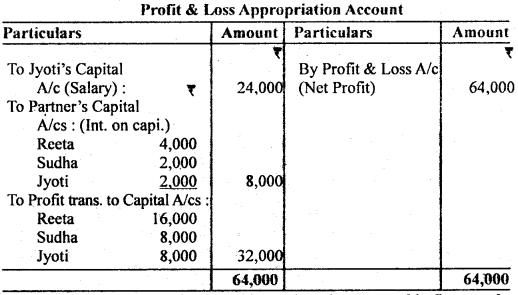
Question 5. Reeta, Sudha and Jyoti were partners in a firm. On 1st January, 2011 their capitals stood at ₹ 40,000, ₹ 20,000 and ₹ 20,000 respectively. As per the provisions of the partnership deed (i) Jyoti was entitled for a salary of ₹ 2,000 p.m. (ii) Partners were entitled to interest on capital at 10% p.a. (iii) Profit to he shared in the ratio of capitals. The profit for the year 2011 was₹ 64,000.
Prepare Profit & Loss Appropriation Account.
Answer:
Question 6. Write the name of occasions when the partnership firm can be reconstituted.
Answer: Occasions of Reconstitution of a Firm :
- Change in the profit-sharing ratio among the existing partners.
- Admission of a new partner.
- Retirement of an existing partner.
- Death of a partner.
- Amalgamation of two (or more) partnership firms.
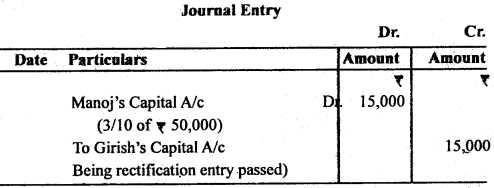
Question 7. Firm of Girish, Jitesh and Manoj earned profits of ₹ 50,000 during the year 2011, which was distributed among the partners in the ratio of 5 : 3 : 2, whereas it should be in the ratio 2 : 3 : 5. Given Journal entry for the rectification.
Answer: Calculation of Gain or Sacrifice share of Partners:
Sacrificing = Old share – New share
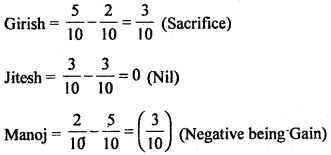
Step 3:
Question 8. What is Revaluation Account? Give the format of Revaluation Account.
Answer: Revaluation Account: devaluation Account is a nominal account. Revaluation Account is credited with the increase in the value of assets and decrease in the value of liabilities. In addition, Revaluation Account is debited with the increase in the value of liabilities and decrease in the value of assets. Excess of credit side over debit side (i.e., profit) or Excess of debit side over credit side (i.e. loss) is distributed among the old partners in their profit-sharing ratio. It should be noted that the new partner is not affected by revaluation of assets and liabilities. After the revaluation, assets and liabilities are shown in the new Balance Sheet at the revised/revalued figures.

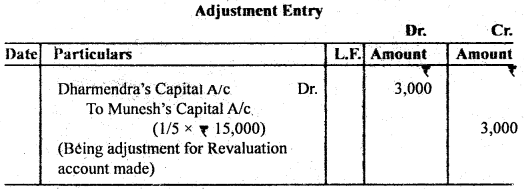
Question 9. Ramesh and Munesh are partners sharing Profit & Loss in the v ratio of 3 : 2. They admit Dharmendra as a new partner. The new ratio is decided to be 3 : 1 : 1. The debit balance of Memorandum Revaluation Account is ₹ 15,000.
Pass an Adjustment entry for the above.
Answer: Calculation of Sacrificing ratio:
Sacrifice = Old Share – New Snare
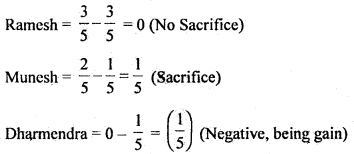
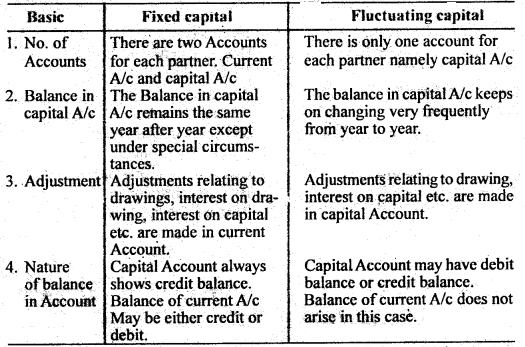
Question 10. Distinguish between Fixed capital and Fluctuating capital.
Answer: Following are the differences between Fixed and Fluctuating capital A/c:
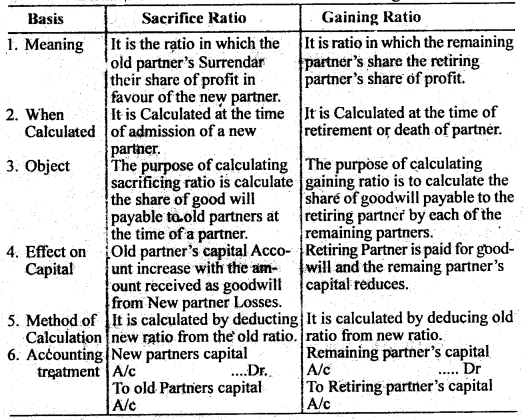
Question 11. Distinguish between Sacrifice Ratio and Gaining Ratio.
Answer: Distinguish between Sacrifice Ratio and Gaining Ratio :
Question 12. Explain any three differences between Dissolution of Partnership and Dissolution of Firm.
Answer: Difference between Dissolution of Partnership and Dissolution of Firm : The partnership Act recognises difference between dissolution of partnership and dissolution of firm. The main points of differences are as under :
1. Change in Relation : The dissolution of the firm implies a complete break-down of the partnership relation between all the partners whereas dissolution of the partnership merely involves a change in the relation of the partners.
2. Continuance of Business: Inn case of dissolution of firm, the business comes to an end whereas in case of dissolution of partnership, the business of the (reconstituted) firm is continued.
3. Effect: Dissolution of partnership does not necessarily mean dissolution of firm whereas dissolution of the firm necessarily implies dissolution of partnership.
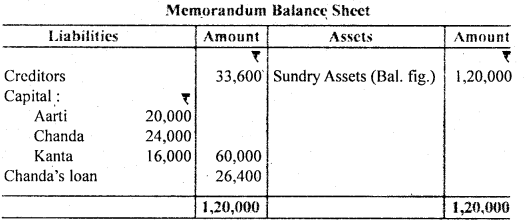
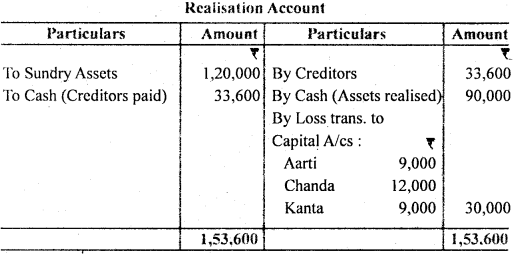
Question 13. Arati, Chanda and Kanta are in partnership sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 4 : 3. They decided to dissolve the partnership firm. At the date of dissolution their creditors amounted to ₹ 33,600. Their capitals stood at ₹ 20,000, ₹ 24,000 and ₹ 16,000 respectively. Chand had lent to the firm in addition to capital ₹ 26,400. The assets realised ₹ 90,000.
Prepare the Realisation Account.
Answer:
Question 14. What is meant by dissolution of partnership? Give two circumstances under which a partnership is dissolved?
Answer: Meaning of Dissolution of Partnership: Any change in the relations of the partners is called the dissolution of partnership. Thus, whenever a new partner is admitted or an old partner retires or dies, a partnership is reconstituted. In all those cases where a partnership is reconstituted, there is a dissolution of the partnership. In case of dissolution of partnership, the firm continues in a reconstituted form.
Reasons of Dissolution of Partnership :
- On retiring of a partners.
- On death of a partners.
Question 15. On the dissolution of a firm 3/4th amount was realised from selling of machine worth ₹ 16,000. Pass entry for realisation.
Answer:

Question 16. Write any three differences between equity shares and preference shares.
Or, Distinguish between Equity Shares and Preference Shares.
Answer: Difference between Preference Shares Equity shares: The difference between preference shares and equity shares are as under:

Question 17. State any three features of a company.
Answer: Essential features of a Company : Following are the essential features (characteristics) of a company :
- Association of Persons : A company is an association of persons, usually for profit.
- Artificial Person : It is an artificial person created by law.
- Separate Legal Entity: It has a separate legal entity from its members. So it can use and can be used in its own name. It can own or dispose of property in its own name.
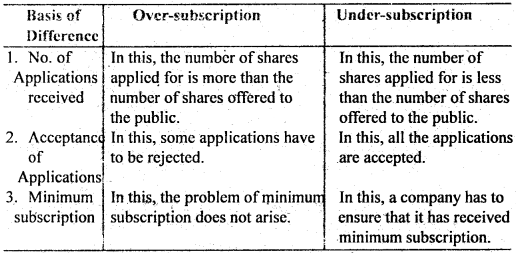
Question 18. Distinguish between Over-subscription and Under-subscription?
Answer: Distinguish between Over-subscription and Under-subscription
Question 19. What are the provisions of reservation for Small Applicants (Investors) by SEBI?
Answer: Reservation for Small Applicants (Investors): In case of over-subscription of shares, as per SEBI guidelines, the following reservation for small individual applications should be kept in mind :
(a) A minimum of 50% of the net offer to public, should be initially made to individual applicants who have applied for 10 or less than 10 marketable lots of the securities offered.
(b) The remaining net offer to public shall be allotted to :
- The individual applicants who have applied for more than 10 marketable lots of the securities; and
- Other investors including corporate bodies or institutions irrespective of the number of shares applied for.
(c) The unsubscribed portion of the net offer made to any of the above mentioned two categories shall may be allotted to other categories. The allotment is to made in marketable lots separately on proportionate basis.
Question 20. What is Buy-back of Shares?
Answer: Buy-back of Shares : A company may buy its own shares from market subject to certain conditions (Sec. 77A). This is known as ‘buy-back’ of shares. Buy-back of equity shares results in the cancellation of share capital and thereby leading to the reduction, in the share capital of the company.
Buy-back of its own shares may be made out of the following :
- Free reserves of the company, e.g., general reserve, reserve fund, credit balance of Profit & Loss A/c.
- The proceeds of any shares or other specified securities.
- Securities Premium Account.
Question 21. Distinguish between Revaluation Account and Realization Account.
Answer: Difference between Revaluation Account and Realization
Realization Account:
- This account is prepared at the time of dissolution of the firm.
- It is prepared to find out profit/loss on the sale of assets and repayment of liabilities.
- After preparation of realization account there will be no business afterwards.
- Realization Account is prepared only once during the lifetime a firm.
Revaluation Account:
- This account is prepared during the reconstitution of the partnership.
- It is prepared to make necessary adjustment regrading revaluation of assets and liabilities.
- After preparing revaluation account business of the firm can be continued.
- Revaluation Account may (if required) be prepared a number of times during the life-time of the firm.
Question 22. What is over subscription of shares?
Answer: Over subscription : when the application money is received for more number of share than the number of shares offered to the public by a company, It is called over subscription. When the shares are over-subscribed, the company cannot satisfy all the applicants. This is due to the reason that the tolal number of shares to be allotted will no case exceed number of shares offered.
Question 23. What is forfeiture of shares. ?
Answer: When shareholder fail to pay allotment or instalment money on shares allotted to them the company has authority to forfeit shares of the defaulters. This is called forfeiture of shares. In case of forfeiture of shares the amount already paid by defaulting shareholder is forfeited by the company.
Question 24. Define prospectus.
Answer: Prospectus: Prospectus may be defined as any notice, circular, advertisement or any other document inviting offers from the public for the purchase of its shares or debentures or for making deposits with it. Thus, a purchase is issued by a company to the public to raise funds. It explains the prospeptus of the company to the general public. Its purpose is to arouse the interest of the investors in the company. It serves as invitations to the public to make deposits with the company or invest in the shares and debentures issued by it.
Question 25. Distinguish between Revenue profit and capital profit.
Answer: Revenue Profit: Revenue profit is the money the business earns through its particular trade. A retail store that sells goods, For example, earns revenue profit when sales of those goods occur. Revenue profit also includes money earned from investments and commission.
Capital Profit: Capital profit is money brought into the company primarily through internal measures. It is profit that is not earned in the regular course of the business. Capital profit includes items such as income from sales of a fixed assets, income from sales of premium share of stock etc.
Question 26. Distinguish between Receipts and payments A/c and Cash Book.
Answer: Distinguish between Receipts and payments A/c and Cashbook are as follows :
Receipts and Payments A/c:
- Entries are not made date-wise.
- Entries are made in classified form.
- This account is prepared at the end of accounting year.
- This is prepared by not-for-profit organisations.
- There is no column of ledger folio.
Cash Book:
- All entries are made date-wise.
- Entries are made in chronological order.
- Cashbook is recorded on daily basis
- This is prepared by all the organisations, trading and non-trading.
- This has a separated column for- ledger folio.
Question 27. What is Unlimited liability?
Answer: Unlimited liability refers to the legal obligations general partners and sale proprietors because they are liable for all business debtsif the business can’t pay its liabilities. General partners and sole proprietors are responsible for paying off all of the company debts. Personally if the company can’t make its payments.
Question 28. What do you mean by issue of shares at discount? State the provisions of Companies Act related to shares issued at discount.
Answer: Shares issued at Discount [Sec. 79]:
Meaning: When shares are issued at a price less than their face value (or nominal value) it is said that they have been issued at discount. For example, if a share of ₹ 10 is issued for ₹ 9, ₹ 1 (₹ 10 – 9) will be treated as discount on issue of shares.
Conditions of Section 79 for issue of shares at Discount:
A company is allowed to issue shares at a discount if the following conditions are fulfilled:
1. The shares must be of a class already issued.
2. The issue of shares at a discount is authorised by a resolution passed by the company and sanctioned by the Company Law Board.
3. The resolution must specify the maximum rate of discount at which the shares are to be issued. The rate of discount must not exceed 10%.
The rate may exceed 10% only if the Company Law Board is of the opinion that a higher percentage of discount may be allowed in the special circumstances of the case.
4. At least one year has elapsed since the company was entitled to commence the business.
5. The issue must be made within two months later receiving sanction from the Company Law Board or within such extended time as the Company Law Board may allow.
Discount on issue of shares is a nominal account. Since it represents a capital loss it is prudent to write it off gradually out of profits over a reasonable number of years.
Question 29. Ram & Co. purchased machinery from Mona & Co. for ₹ 4,00,000. A sum of ₹ 1,75,000 was paid by the means of a bank draft and for the balance due Ram & Co., issued Equity Shares of ₹ 10 each at a discount of 10%.
Journalise the above transactions in the hooks of the company.
Answer:
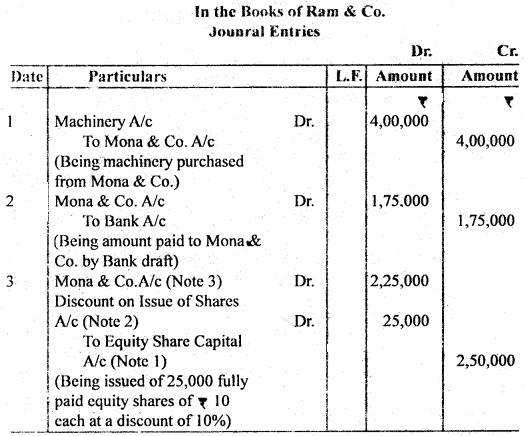
Working Notes :

2. Discount = 2,50,000 × 10/100 = ₹ 25,000
3. ₹ 4,00,000 – 1,75,000 = ₹ 2,25,000
or, ₹ 2,50,000 – 25,000 (Discount) = ₹ 2,25,000
Question 30. What is Redemption of Debentures?
Answer: Meaning of Redemption of Debentures :
Redemption of debentures means discharge of liability on account of debentures. Usually, debentures are redeemed at the expiry of their life in accordance with the terms and conditions. The terms are clearly stated in Debenture Certificate. So a company is under obligation to make payment Of the amount due on debentures to the debenture holders.
The following three major issues should be dealt with by a company regarding redemption of debentures :
- Determination of Time of Redemption;
- Computation of Amount of Redemption;
- Determination of the Sources of Redemption.
Question 31. State any three objectives of Financial Statement
Or, What are the objectives of Financial Statements?
Answer: There are following objectives of Financial Statements :
- To serve as a media of information regarding profitability and financial health of the enterprise.
- To assist in investment decision-making.
- To help in planning.
- To help management in assessing the efficiency of the organisation.
- To provide financial information about economic resources and obligations of a business enterprise.
- To provide reliable information about changes in net resources (that is, resources less obligations) arising out of business activities.
- To assist in estimating the earnings-potentials of the business.
- To disclose other information that is relevant to the needs of the users of the financial statements.
Question 32. What is Financial Statements?
Or, What do you mean by Financial Statements?
Answer: Meaning of Financial Statements: The end product of financial accounting is financial statements. Financial Statements are organised summaries of detailed information about financial position and performance an enterprise for a particular period. Financial Statements are also called financial reports. The financial information of an enterprise is contained in the financial statements or accounting reports. The term ‘Financial Statements’ normally refer to two basic statements, namely:
- Balance Sheet (or Statement of Financial Period),
- Profit & Loss Account (or Income Statement).
According to John N. Myer, “The financial statements provide a summary of the accounts of a business enterprise, the Balance Sheet reflecting the assets, liabilities and capital as on a certain date and the income statement showing the results of operation during a certain period.”
Question 33. What is meant by Financial Statement Analysis?
Or, Explain the meaning of Analysis of Financial Statement.
Answer: Meaning of Analysis of Financial Statements : Analysis is the process of critically examining the accounting information given in financial statements. For the purpose of analysis, individual items are studied, their inter-relationship with other related figures is established. Sometimes the data are re-arranged to have a better understanding of the information with the help of different techniques or tools for the purpose.
Hence, analysis of financial statement is a process of evaluating relationship between component parts of financial statements to obtain a better understanding of the information with the help of different techniques or tools for the purpose. Hence, analysis of financial statement is a process of evaluating relationship between component parts of financial statements to obtain a better understanding of firm’s position and performance.
In the words of Finley and Miller, “Financial analysis consists of separating facts according to some definite plan, arranging them in groups according to certain circumstances and then presenting them in a convenient and easily readable and understandable form.”
Thus, analysis of financial statement implies classifying, arranging and comparing the information given in financial statements.
Question 34. Explain the features of Financial Analysis.
Answer: Features of Financial Analysis: The following are the features of financial analysis :
- To present the complex accounting data in simple and understandable form.
- To classify the items given in Profit & Loss Account in convenient and related groups.
- To classify the items given in the Balance Sheet in convenient and related groups.
- To make comparisons between different groups to interpret different conclusions.
- To convert the mass of financial data into useful information which is always in scarce supply.
Question 35. Write the objectives of Analysis of Financial Statements.
Answer: Objectives or Purposes of Financial Analysis: The main objectives (or purposes) of analysis of financial statements are as follows :
- To assess the present and future earning capacity or profitability.
- To assess the operational efficiency of the concern as a whole or of its various parts or departments.
- To assess the short-term solvency of the concern.
- To assess the long-term solvency of the concern.
- To compare intra-firm position and inter-firm position.
- To locate the areas of efficiency or deficiency.
- To assess the financial stability of a business concern.
- To assess the long-term liquidity of its funds.
- To determine the value of business,
- To determine the value of goodwill.
- To assess the possibility of developments in the future by making forecasts and preparing budgets.
- To judge the efficiency of management.
- To take corrective action on the basis of information so gathered.
Question 36. From the following particulars, calculate the Inventory Ratio for each year :
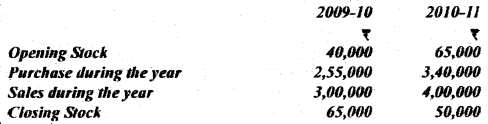
Answer:
(i) Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchase – Closing Stock
For 2009-10 = ₹ 40,000+ 2,55,000 – 65,000 = ₹ 2,30,000
For 2010-11 = ₹ 65,000 + 3,40,000 – 50,000 = ₹ 3,55,000
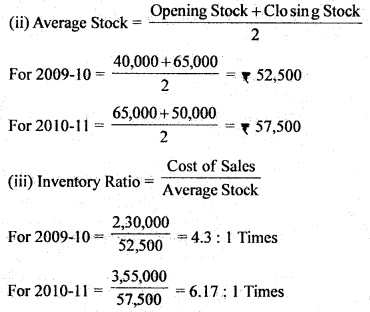
Question 37. What do you mean by Cash How Statement ? Explain.
Answer: Meaning of Cash Flow Statement : A statement of change in financial position on cash basis is commonly known as the cash flow statement. It shows the changes in cash position from one accounting period to another. In other words, cash flow statement summarises the causes of changes in cash and cash equivalents position between dates of two Balance Sheets. It indicates the source and uses of cash. This statement attempts to analyse the transactions of the firm in terms of cash.
Thus, a Cash Flow Statement can be defined as a statement which summarises sources of cash inflows and uses of cash outflows of the firm during a particular period of time, say, a month or a year.
Question 38. How is Cash flow from Operating Activities calculated?
Answer: Calculation of Cash Flow from Operating Activities: Almost all the companies prepare its Income Statement on accrual basis of accounting under which revenues are recorded when earned and expenses are recorded when incurred. Because of this, net profit, as shown by Income Statement will not be equal to cash generated by operating activities. Hence, there is aneed to calculate cash flows from operating activities. AS-3 (Revised) suggests two methods of reporting cash flows from operating activities :
- Direct Method, and
- Indirect Method.
1. Direct Method : Under direct method major classes of gross cash receipts and gross cash payments are considered. Under this method, cash receipts from operating, activities, i.e., cash received from the sale of goods and rendering services, cash collected from customers and cash received from trading commission and royalties and cash payments for operating activities such as payment to creditors for goods and services, employees for their services etc. are disclosed. The difference between cash receipts and cash payments is the net cash flow from operating activities. A cash flow statement based on direct method is a Profit & Loss Account on cash basis.
2. Indirect Method : Under this method, net profit or loss is adjusted for the effects of transactions of non-cash nature and non-operating nature and changes in current assets and liabilities.
Question 39. What is Cash Flow from Investing Activities?
Answer: Cash Flow from Investing Activities : Cash flow from investing activities are the cash flows from the transactions involving purchase and sale of resources, i.e. long-term productive assets intended to generate future income and cash flows.
Examples of Cash Flow from Investing Activities : AS-3(Revised) :
- Cash payments to acquire fixed assets including intangible assets such as goodwill, patents and copyrights. It also includes payment made to construct fixed assets.
- Cash receipts from disposal of fixed assets including intangibles.
- Payment to acquire shares or debentures, investments.
- Cash receipts from sale of shares, debentures etc. of other companies.
- Cash advances and loans made to third parties (other than loans and advances made by a financial enterprise).
Question 40. What are the objectives of Cash Flow Statement?
Answer: The main objectives of preparing Cash Flow Statement are as follows:
- To throw light on specific sources of Cash Flow.
- To ascertain the specific uses.
- To ascertain the net change in Cash and Cash Equivalents.
- To disclose changes in cash position.
- To determine cash requirement.
- For efficient cash management.
- To judge liquidity position.
- To help in short-term planning.
- To analyse financial position.
- To help in dividend decision.
Question 41. From the following particulars, compute cash in operation:

Answer:

Question 42. Calculate cash flow from the following financing activities :

Additional Information : (i) Equity shares were issued at a premium of 20%. (ii) 12% preference shares were redeemed at a premium of 10%. (iii) 10% Debentures were issued at a discount of 1%. (iv) Interim dividend paid of equity shares ₹ 90,000.
Answer:
Calculation of Cash Row From Financing Activities
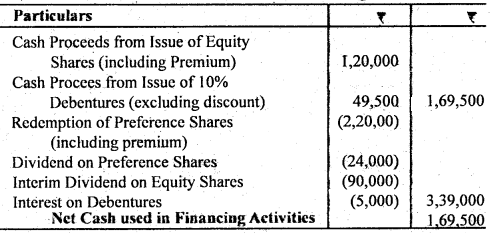
Assumptions :
- Preference shares are redeemed at year end.
- Debentures are issued at beginning of year.
Question 43. The following is the position of Current Assets and Current Liabilities of Vijay Ltd. :

The company incurred a loss of ₹ 6,000 during the year. Calculate Cash Flow from Operating Activities.
Answer:
Calculation of Cash Row from Operating Activities
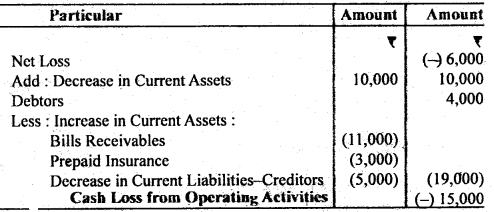
Question 44. From the following particulars, calculate Cash How from Investing Activities:

During the year the company had sold 50% of its investment held in the beginning of the period at a profit of ₹ 90,000.
Answer:

2. Investment Account

Question 45. The following is the position of current assets and current liabilities of X Ltd.:

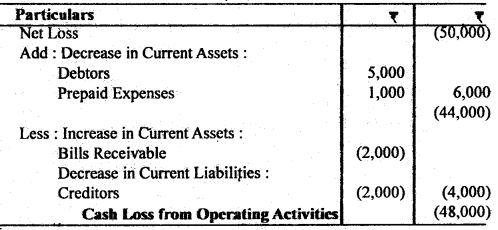
The company has incurred a loss of ₹ 50,000 during the year. Calculate cash from operations.
Answer:
Question 46. State the features of income and expenditure A/c.
Answer: Features of income & expenditure A/c :
- It is a normal account.
- It is prepared from the receipts and payments account and other relevent information (or additional information)
- All revenue expenses related to current year are recorded on the debit side of the income & expenditure A/c.
- All revenue incomes related to current year are shown on the credit side of income & expenditure A/c.
- Items of capital nature are not shown in this account,
- Like P/L A/c it also includes the non-cash items, such as depreciation, provision for bad and doubtful debts etc.
- It shows income & expenditure of current year only on accrual basis.
- The balance at the end of the year represents surplus or deficit.
Question 47. State the uses of Cash Flow Statement?
Answer: Along with balance sheet and income statement, the investment of cash flows would assits the users of financial statements the following way :
- To analyse the reasons for change in cash balance of the enterprise.
- To judge the enterprise ability to pay its debts, to pay dividends to its shareholders and to pay interest on loans.
- To assess the enterprise’s need to borrow cash.
- To find out the reasons for difference between the enterprise net income, cash payment and cash receipts.
- To analyse reasons for change in enterprise’s financial position including investing and financial activities during a period of time.
Question 48. Explain three factors affecting goodwill.
Answer: Three factors effecting goodwill are as follows :
- Efficiency of management: If the business is managed by capable and competent persons, then the value of goodwill will be high.
- Nature of goods : If the business of a firm is of the nature where the goods dealt in are in high demand although not in short supply. The profits will be higher. It results is increase in the value of goodwill.
- Location : If the business is located at a renowned place, the goowill will increase.
Question 49. What is meant by comparative financial statement?
Answer: Comparative Financial Statement is a tool of financial analysis. Any financial statement that presents the comparison of date of two or more years is known as comparative financial statement.
Question 50. What is sacrificing ratio? Why is it Calculated?
Answer: The ratio in which the old partners have agreed to sacrifice this shares in profits in favour of new partners is called the sacrificing ratio. In principle, the sacrifice ratio is the difference between the old profit sharing ratio and the new profit sharing ratio.
Sacrificing Ratio = Old Ratio – New Ratio
The new partner is required to compensate the old partners for the sacrifice of share in the profits of the firm for which he brings in an additional amount known as premium or goodwill. This amount shared by the old partners in the ratio in which they for go their share in favour of the new partner which is know as sacrificing ratio.