Bihar Board 12th Accountancy Important Questions Short Answer Type Part 1 in English
Bihar Board 12th Accountancy Important Questions Short Answer Type Part 1 in English
BSEB 12th Accountancy Important Questions Short Answer Type Part 1 in English
Question 1. What is current assets?
Answer: Current assets are cash and other such assets which can be converted into cash within a short period (Normally within one year). Thus current assets = Cash + Cash at Bank + Bills Receivable + Closing Stock + Short term Investment + Sundry Debtors + Prepaid Expenses.
Question 2. Define Sinking fund.
Answer: A Sinking fund is a fund which is created out of profit every year and invested in marketable securities carrying fixed rate of interest. Interest earned on the investment is also invested in such securities. On the date of redemption, investments so made are sold in the market.
Question 3. Distinguish between Current Ratio and Quick Ratio.
Answer: Difference between Current Ratio and Quick Ratio :
| Current Ratio | Quick Ratio |
| (i) Current Ratio show the relationship between Current Assets (C.A) and Current Liabilities (C.L.) | (i) Quick Ratio shows the relationship between Liquid Assets (L. A.) and Current Liabilities (C.L.) |
| (ii) Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities | (ii) Quick Ratio = Liquid Assets / Current Liabilities |
| (iii) The objective of the current ratio is whether an organisation can pay off its current liabilities out of its current assets within a short time i.e., a year or not. | (iii) Current Liabilities The objective of quick ratio is to ascertain whether the firm shall be able to discharge its current liabilities quickly, that is within a month or immediately. |
| (iv) The ideal current ratio is 2 : 1. | (iv) The ideal Quick Ratio is 1 : 1. |
Question 4. Explain four characteristics of a partnership.
Answer: For characteristics of partnership are as follows :
- Two or more persons: The minimum number of partners in a firm can be two but there should be not more than 10 persons in the case of banking business and 20 in the case of any other business.
- Agreement: There should be an agreement between the partners. This agreement may be oral, written or implied.
- Profit-sharing: The agreement between the partners must be with the objects of sharing profits among all the partners. An agreement to share losses is not essential.
- Mutual Agency: Business of the partnership must be carried on by all the partners or by one of them acting for all, that is, there must be mutual agency. Thus, every partner is both an agent and the principal for himself and other partners.
Question 5. What is super profit?
Answer: Super profit is the excess of average profit of the business Over the normal profit.
Super profit = Average Actual Profit – Normal Profit.
Question 6. What is Financial statements ?
Answer: Financial statements are those statements of a company that depict the financial position and result of business activities at the end of the accounting period. The financial statements of a company are also called annual Reports, Anual Accounts or published Accounts. Ex-Balance sheet, statement of profit & Loss, Cash Flow statements.
Question 7. What is Revaluation Account?
Answer: Revaluation Account is prepared to find out profit or loss on revaluation of assets and re-assessment of liabilities at the time of reconstitution of partnership firm. Profit or loss arising from revaluation is shared by the old partners in their old profit-sharing ratio.
Question 8. What is Receipts and Payments Account?
Answer: Receipts and Payments Account is a summary of Cash Book. All cash receipts and payments are recorded in this account. Receipts and Payments recorded in this account may be either of revenue nature or capital nature.
Question 9. What is meant by Income and Expenditure Account?
Answer: Income and Expenditure Account is a summary of revenue income and expenses and losses of a not for profit organisation for a particular period. The balance of this account shows either ‘Surplus’ or ‘Deficit’.
Question 10. What is sacrificing ratio?
Answer: The ratio in which the old partners have agreed to sacrifice their shares in profit in favour of a new partner is known as sacrificing ratio.
Question 11. How is goodwill recorded at the time of retirement of a partner?
Answer: The retiring partner’s share of goodwill is credited to his account and debited to remaining Partners’ Capital Accounts in gaining ratio.
Remaining Partner’s Capital A/c Dr. (in Gaining Ratio)
To Retiring Partner’s Capital A/c
Question 12. What is Surrender Value?
Answer: Surrender value is the value which insurance company will pay, if the policy is discontinued and surrendered to the company before the date of maturity.
Question 13. State any two circumstances under which partnership is deemed to have been dissolved.
Answer:
- On the expiry of the period of partnership
- On admission, retirement or death of a partner.
Question 14. What is Realisation Account?
Answer: Realisation Account is a nominal account. It is prepared to find out profit or loss on realisation of assets and payment of liabilities. The profit (or loss) on realisation is transferred to Partners’ Capital Accounts in their profit-sharing ratio.
Question 15. What do you mean by Preference Shares?
Answer: Preference Shares are those shares which have the following two preferential rights:
- Right to receive divided at a fixed rate.
- Right to the repayment of capital on the winding up of the company.
Question 16. What is Share Premium?
Answer: According to Section 78 of the Companies Act, 1956 a company issuing securities (shares, bonds or debentures) at a premium whether for cash or for a consideration other than cash, should credit a sum equal to the aggregate amount of the premium on the securities, to a separate account called ‘Securities Premium Account’.
Question 17. What is buy-back of shares?
Answer: Buy-back of shares implies purchasing of its own shares by a company It may be made out of the (i) free reserves, (ii) securities premium, or (iii) proceeds if any shares or securities.
Question 18. What is Right Issue of Shares?
Or, What do you mean by Right Issues of Shares?
Answer: Under section 81 of the Companies Act, 1956, the existing shareholders have a right to subscribe in their existing proportion to the fresh issue of capital.
Shareholders may accept this offer or reject the offer or sell their rights. Such issues are called Right Issues of Shares.
Question 19. What is meant by authorised capital of a company?
Answer: Authorised capital is the capital stated in the Memorandum of Association (MOA). It is the maximum amount of capital which a company can raise during its life time.
Question 20. What is minimum subscription?
Answer: Minimum subscription means the minimum amount that must be received by the company stated in the prospectus otherwise shares cannot be allotted. In general, it is 90% of the issued amount.
Question 21. What is meant by forfeiture of shares?
Answer: When shareholders fail to pay allotment or instalment money on shares allotted to them, the company has authority to forfeit shares of the defaulters. This is called ‘forfeiture of shares’. In case of forfeiture of shares, the amount already paid by defaulting shareholder is forfeited by the company.
Question 22. What is meant by debenture?
Answer: Debenture is a written instrument (document) issued by a company acknowledging a debt. It contains provision as regards the repayment of principal and the payment of interest at a fixed rate. Debentures include “debenture stock, bonds and other securities”.
Question 23. What is meant by redemption out of capital?
Answer: When adequate profits are not transferred from Profit & Loss Appropriation Account to the Debenture Redemption Reserve Account, at the time of redemption of debentures, such redemption is said to be out of capital.
Question 24. State in brief, SEBI guidelines relating to creation of ‘Debenture Redemption Reserve Account’.
Answer: As per SEBI guidelines, a company is required to create a Debentures Redemption Reserve Account equivalent to 50% of the amount of debenture issued before redemption of debentures Commences.
Question 25. What is meant by financial statement?
Answer: Financial statements are the annual reports which present financial information about the performance and financial position of a business enterprise.
Question 26. State any three qualities of good financial statements.
Answer:
- Comparative Study.
- Knowledge about Future Earning Capacity.
- Information regarding Important Activities.
Question 27. What is Income Statement?
Or, What is Profit & Loss Account?
Answer: Income Statement (or Profit & Loss Account) is the accounting report which shows the revenues and expenses and ascertains the profit/loss for a specified accounting period.
Question 28. What is meant by Financial (Statement) Analysis?
Or, Explain the meaning of Analysis of Financial Statements.
Answer: Analysis of financial statements is a systematic study of the information contained in the financial statements of the business enterprise in order to assess its financial health and future prospects.
Question 29. What is meant by horizontal analysis?
Answer: When the financial statements of a number of years are to be analysed, horizontal analysis is made. Under this type of analysis, the items of current year are compared with the items of the previous years. Comparative statements are the example of horizontal analysis.
Question 30. What is meant by vertical analysis?
Answer: When financial statements of a particular year or on a particular date are analysed component-wise, it is called vertical analysis. For example, in common-size statements vertical analysis is made.
Question 31. What do you mean by Comparative Income Statement?
Answer: Comparative Income Statement shows increase or decrease in absolute figures of the incomes and expenses. It reflects absolute and percentage change in the operating activities of the business firm for two or more accounting periods.
Question 32. State the major heads under which the items appearing on the liabilities side of a Company’s Balance Sheet are classified.
Answer: Major heads on Liabilities side of a Company’s Balance Sheet are as under:
- Shareholder’s Funds
- Share Application Money pending allotment
- Non-current Liabilities
- Current Liabilities.
Question 33. What is meant by Cash Equivalents?
Or, What are Cash Equivalents?
Answer: Cash equivalents are the highly liquid short-term investments which are rapidly converted into known amount of cash without any risk of changes in value. For example, Government securities, Treasury bills etc.
Question 34. What do you mean by Accounting Ratios?
Answer: The term ‘accounting ratios’ is used to describe relationship between two figures are group of figures shown in the financial statements (i.e., Balance Sheet and Income Statement).
Question 35. Give the definition of the partnership.
Answer: Partnership is an association of persons who agree to combine their financial resources and managerial abilities to run a business and share the profit of that business in an agreed ratio.
According to sec. 4 of the Indian partnership act, 1932, “the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all.” The persons who have entered into partnership with one another, are individually called partners and collectivity called firm. The name in which the partnership business is carried on is called the firm’s name.
Question 36. Explain the importance of partnership deed.
Answer: The importance of partnership deed ate as follows :
- Helpful in smooth functioning of the business.
- Useful in resolve disputes and misunderstandings among partners.
- Useful in regulating the duties and responsibilities of each partner.
- If there is any dispute among the partners, the partnership deed will serve as an evidence in the court of law.
Question 37. What do you mean by profit’& loss appropriation account?
Answer: The net profit (after adjustment of partner’s transactions such as interests on capital, partner’s salary, commission drawings, interest on drawings etc.) is to be shared by all the partners in the agreed profit sharing ratio. For this purpose, a separate account is prepared for distribution of profits between j the partners, known as profit & loss appropriation account.
Question 38. Explain the nature of goodwill.
Answer: Like buildings, machinery and furniture etc. goodwill is also an asset, but the main point of difference is that building etc. can be seen and touched while goodwill cannot be seen and touched but felt, it is invisible hence it is treated as an intangible asset. All assets can be separately sold but goodwill cannot be separately sold. This is why, goodwill has no separate existence while other assets have. Hence, it is not a fictitious asset as it can be purchased or sold with any other asset.
Question 39. What do you mean by retirement of a partner?
Answer: A partner may wish to withdraw from a firm for various reasons like old age. Change of residence, on health ground, misunderstanding with other partners or any other reason. Such a situation is called retirement of a partner. So it means to leave the firm. Any such type of partner is known as retiring partner.
Question 40. Give the meaning of death of a partner.
Answer: When a partner dies, it means compulsory retirement and his representatives or the execution of his estate are entitled to all the rights. The representatives of the deceased partner will be entitled to his share of profit accrued upto the date of death.
Question 41. What do you mean by dissolution of partnership firm?
Answer: Dissolution of firm means discontinuance of economic relation between the partners. According to see 39 of Indian partnership act, 1932, “dissolution of firm means dissolution of partnership between all the partners in the firm.” When the complete business of the firm is closed down due to any reason, it is called dissolution of the firm.
Question 42. What are the modes of dissolution of a partnership firm?
Answer: The modes of dissolution of a partnership firm are as follows :
- Dissolution by agreement
- Compulsory dissolution
- Dissolution on the happening of certain contingency.
- Dissolution by notice Gn case of partnership at will.
- Dissolution by a court.
Question 43. What do you mean by share of a company?
Answer: The capital of a company is divided into a number of equal parts. Each part is called a share. A company many divide its capital into shares of 1, 2, 5, 10 or any suitable amounts (or denomination).
Question 44. What is preference share?
Answer: Preference share is on which carries the following two rights as per section 85 of companies act:
- They have a right to receive dividend at a fixed rate before any divided is paid on the equity shares.
- One the winding up of the company, they have right to return of capital before that of equity shares.
Question 45. What is equity share?
Answer: Under Indian companies act, 1956, “an equity share is a share which is not a preference share.” Thus, this share does not carry any preferential right. In other words, equity share is one which is entitled to dividend and repayment of capital after the claims of preference shares are satisfied.
Question 46. Give the definition of debenture.
Answer: According to sec. 2(12) of Indian companies act. 1956. “Debenture includes debenture stock, bonds and any other securities of a company whether constituting a charge on the assets of the company or not.” According to Topham, “Debenture is a document given by a company as evidence of a debt to the holder usually arising out of a loan and most commonly secured by a charge.”
Question 47. What do you mean by redemption of debentures?
Answer: Redemption of debentures means the repayment of the amount of debentures to debenture holders. In otherwords, redemption refers to discharge of liability on account of debentures by paying the due amount of debenture. The redemption of debentures is made by the company in accordance with the terms and conditions of issue which are clearly stated in the departure certificate.
Question 48. Give the definition of financial statement analysis.
Answer: According to finnery and miller, “Financial analysis consists in separating facts according to some definite plan, arranging then in group according to certain circumstances and then presenting them in a convenient and easily read and understandable form.”
According to John Myers “Financial statement analysis is largely a study of relationship among the various factors in a business as disclosed by a single set of statement and a study of the trends of these factors, as shown in a series of statements.”
Question 49. What is ratio analysis?
Answer: An analysis of financial statement with the help of ratio may be termed as ratio analysis. The ratio analysis is a very powerful analytical tool useful for measuring performance of a business enterprise. Thus, ratio analysis implies the process of computing, determining and presenting the relationship of items and groups of items in the financial statements.
Question 50. What do you mean by cash flow statement?
Answer: Cash flow statement deals with the preparation and presentation of statement of changes in cash flows during a particular period. In other words, it is a summary of source and application of cash during a particular span of time. Thus, it analyses the reasons for changes in balance of cash between two balance sheet dates.
Question 51. Explain cash flow from operating activities.
Answer: Operating activities are the main source of revenue and expenditure in an enterprise e.g., for a company manufacturing garments, purchase of raw material, payment of wages, sale of garments etc. therefore, they generally result from die transactions and other events that enter into the determination of net profit or net loss.
Question 52. Explain cash flow front investing activities.
Answer: Investing activities rotate to fixed assets, e.g., purchase and sale of land, building, computer, furniture, long term investment etc. As per As-3 investing activities are the acquisition and disposal of long term assets and other investments not included in cash equipments. Long term assets are there which are not kept for re-sale, e.g., building, furniture, machinery, plant etc.
Question 53. Explain cash flow from financing activities.
Answer: Financing activities are those which are related to long term equity and liabilities of an enterprise, i.e., cash receipts from issue of shares, debentures, raising long term loans and redemption of that loan etc. As per As-3, financing activities are activities than result in changes in the size and composition of the owner’s capital and borrowings of the enterprise.
Question 54. Explain the limitations of cash flow statements.
Answer:
- Cash flow statement is only a supplementary statement and cannot replace the income statement.
- Cash flow statement cannot be equated with income statement.
- Cash flow statement ignores non-cash items.
- The cash balance as disclosed in the cash flow statement may not represent the real liquid position of the business.
Question 55. Give three feature of Receipts and Payments Account.
Answer: Features of Receipts and Payments Account:
- It is areal account.
- It is the summary of Cash and Bank transactions.
- All the receipts (whether they are of capital nature or revenue nature) are shown on the debit side of this account.
Question 56. Distinguish between Income and Expenditure Account and Profit & Loss Account.
Answer: Distinction between Income & Expenditure Account and Profit & Loss Account:
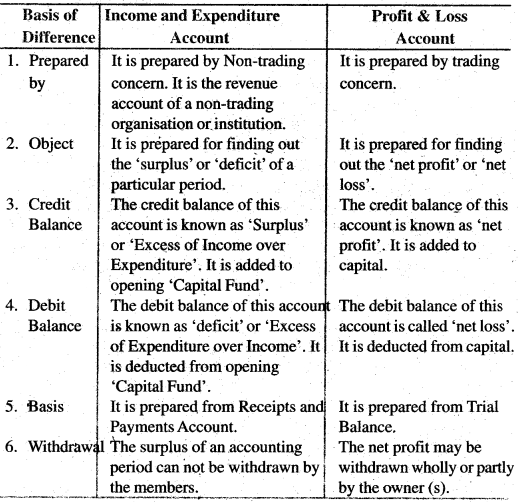
Question 57. Difference between Receipts and Payment Account and Cash Book.
Answer: Difference between Receipts and Payment Account and Cash Book:
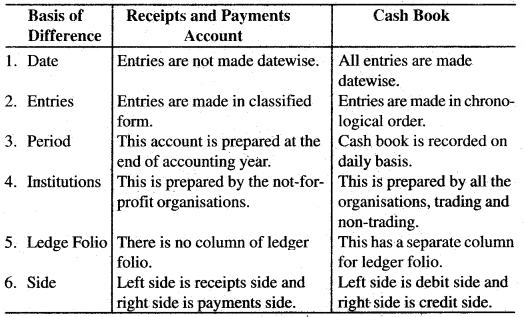
Question 58. State six features of Income and Expenditure Account.
Answer: Features of Income and Expenditure Account:
- It is a nominal account.
- It is prepared from the Receipts and Payments Account and other relevant information (or additional information).
- All revenue expenses related to current year are recorded on the debit side of the Income and expenditure account.
- All revenue incomes related to current year are shown on the credit side of Income and Expenditure Account.
- Items of capital nature are not shown in this account.
- It shows income and expenditure of current year only on accrual basis.
Question 59. What is Receipts and Payments Account?
Answer: Meaning of Receipts and Payments Account: A Receipts and Payments Account is a summary of cash receipts and cash payments relating to a given period. It is, in fact, a summary of the Cash Book. It is prepared at the end of the period under consideration. All receipts (relating to past, present or future period) are shown on the debit 6ide and all payments (relating to past, present or future) are shown on the credit side of this account.
It should be noted that in Receipts and Payments Account both revenue and capital items are shown. It does not give the date of transactions. Thus, both Cash Book and Receipts and Payments Account provide the same information but in different manner. Hence, in some respects they differ from each other.
Question 60. From the following information., prepare a Comparative Income Statement:

Answer:

Question 61. What are the limitations of Common-size Statements?
Answer: Following are the main limitations of common-size statements :
- Difference between Different Activities : The use of this method is not possible when the various activities of a concern differ from each other.
- Difference in Accounting Methods : If the accounting methods followed by two businesses are different, this method of analysis can not be used.
- Difference in Heads of Account: If there is a difference between the various heads of accounts, i.e., different expenses are treated and written or collected, this method may give misleading conclusions.
Question 62. Prepare common-size income statement of AB Ltd. with the help of the following information :
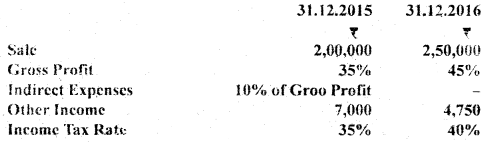
Answer:

Question 63. What is Profitability Ratio? Explain.
Answer: Profitability Ratio : Profitability refers to the ability of a business to earn profit. It shows the efficiency of the business. These ratios measure the profit earning capacity of the company. Profitability has direct link with sales. This is why, we calculate these ratios on the basis of sales. Return on investments and capital is calculated on the basis of capital employed. Generally profitability ratio is calculated in percentage (%).
Generally, three types of profitability ratios are calculated :
- Profitability Ratios based on Sales.
- Profitability Ratios based on Investments or Capital Employed.
- Profitability Ratios based on Earning on Shares.
Some important profitability ratios are as under :
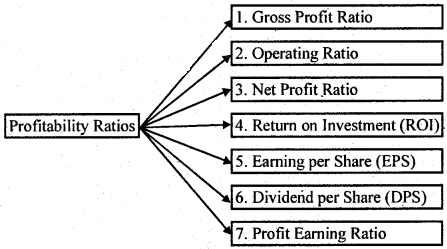
Question 64. Explain any three limitations of the Ratio Analysis.
Answer: The limitations of Ratio Analysis are as follows :
- False Results : Rati0s are based upon the financial statements. In case, financial statements are incorrect or the data upon which ratios are based is incorrect, ratios calculated will also be false and defective.
- Limited Comparability : The ratio of the one firm can not always be compared with the performance of other firm, if uniform accounting policies are not adopted by them.
- Lack of Standard Universally accepted Terminology : The ratio can be comparable only when uniform terminology is adopted by both the firms.
Question 65. What does Debt-Equity Ratio indicate?
Answer: Debt-Equity Ratio : Debt-equity Ratios shows a relationship between long-term debts and shareholders’ funds. In other words, this ratio indicates the relationship between outsiders’ funds (i.e., lenders’ contribution) and shareholders’ funds (i.e., owner’s contribution). It is also known as External-Internal Equity Ratio. This ratio is calculated to measure the relative claims of outsiders and the shareholders against the firm’s assets.
Computation : It is calculated on the basis of the following formula :
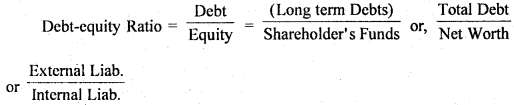
Shareholder’s Funds or Net Worth or Equity Debt or Long term Debt = (Equity Share Capital + Preference Share Capital + Capital Reserve + Revenue Reserve + Reserve for Contingencies + Retained Earnings + Sinking Funds) – Fictitious Assets such as accumulated losses and deferred expenses
= Debenture + Mortgage Loans + Bank Loan + Public Deposits and Other Long-term Loan